Development
What is development?
Human development refers to the progress that people and communities make in improving their general wellbeing. Development measures indicators including health, education, living standards, rights, and the opportunities individuals have to live safe, productive, and meaningful lives.
Development is concerned with quality of life, not just economic growth.
A lack of development can be caused by environmental, social, economic, and political factors.
Environmental factors, such as available resources and food sources, climate conditions, frequency of natural disasters, diseases.
Social factors including traditional religious and cultural beliefs, political instability, the societal status of women and population trends
Economic factors include the level of industrialisation and urbanisation.
To do:
Define development in your own words
Create a diagram that explains the three factors causing a lack of development (inequality).
1. Measuring development
Activity 1: Understanding development indicators
We use indicators to measure development (wellbeing). Development indicators measure the factors that shape people’s lives. Factors such as GDP per capita, occupation and housing, and then balancing these with quality of life indicators such as health status, employment, education, civil engagement, personal security and environment quality, Geographers aim to get a broad picture of the level of development in a country or region.
Indicators are useful to geographers.
For showing where lack of development is impacting communities.
Identifying areas that are improving and can be further supported.
Revealing correlations and relationships.
To do: questions
Define development indicators.
Explain the difference between single and composite indicators using two examples.
Identify two possible problems with development indicators.
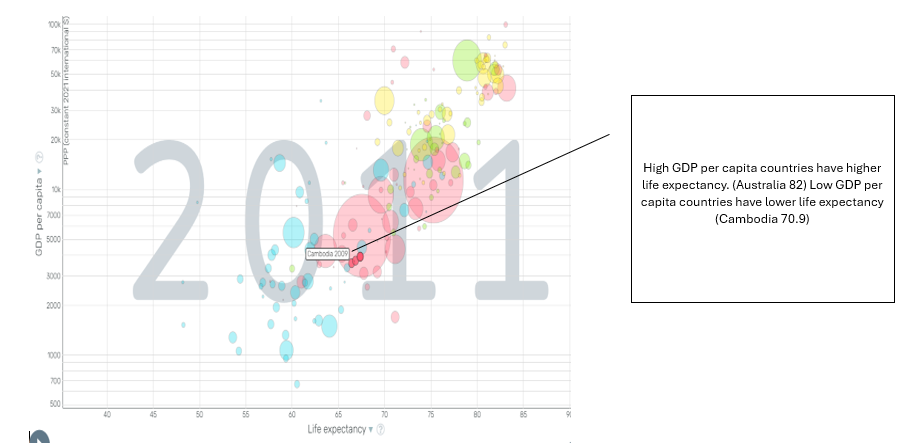
Describe the spatial variation in global life expectancy and the HDI. (Use graphs below)
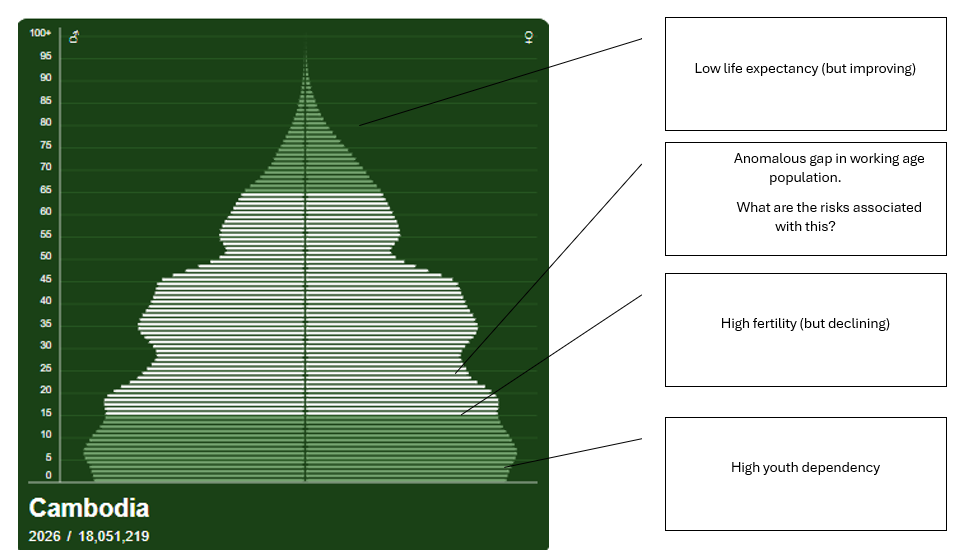
Describe the trend in the global fertility rate. (Use graphs below)
Activity 2: Visualising (under) development with Gapminder
What does a lack of development look like?
1. Use Gapminder.org to create scatter graphs that compare Cambodia’s GDP per capita PPP with the following indicators. Save and annotate the graphs.
○ Literacy rate / GDP per capita PPP
○ Life Expectancy / GDP per capita PPP
○ Access to fresh water (basic) / GDP per capita PPP
○ Primary completion rate female / GDP per capita PPP
2. List three social (health) impacts for each of the following indicators.
○ The health impacts of the lack of safe drinking water
○ The health impact of lack of sanitation
○ The social impacts of gender inequality in education
○ The economic impacts of insecure shelter / housing
Activity 3. Visualising development in an LEDC
‘What gets measured gets managed’. Peter Drucker
Before you can begin to support development you need to measure it.
There are a number of ways you can do this.
To do: Create an annotated folio using the following indicators, to describe the current state of development in your chosen LEDC.
Include the following annotated graphs (indicators) in your country development assessment.
2. Barriers to development
Barriers to development.
Countries are rich or poor due to differences in natural resources, history, education, governance, and global connections. Wealthier nations often have stable governments, strong industries, good infrastructure and education systems, while poorer nations may face poor governance, conflict, limited resources, or environmental challenges that restrict development and opportunities.
Why some countries are rich…..
Strong public institutions
A strong legal framework
Merit based government and semi government career paths
A positive cultural (religious) outlook
Geographical advantages
and some are poor.
Weak public institutions
Weak legal framework (corruption & lack of property rights)
Clan based government and semi government hiring policies
A traditional /conservative cultural (religious) outlook
Geographical disadvantages
To do. Questions. Why are some countries poor?
Watch the video, list the reasons some countries are rich and some are poor.
Define public institutions, explain their importance for development.
List the ways a strong legal framework benefits development?
Extra: Many MEDC’s have corruption issues, how do they overcome this barrier?
Background briefing: Barriers to development
Use a country example to illustrate your response to each of the following questions.
How do weak public institutions act as barriers to development?
How does corruption lead to underdevelopment?
Define a traditional cultural/religious outlook and describe the potential impact of this outlook on the people of rural Chad.
List the negative impacts of clan based government hiring policies.
How do geographical (physical) disadvantages contribute to underdevelopment?
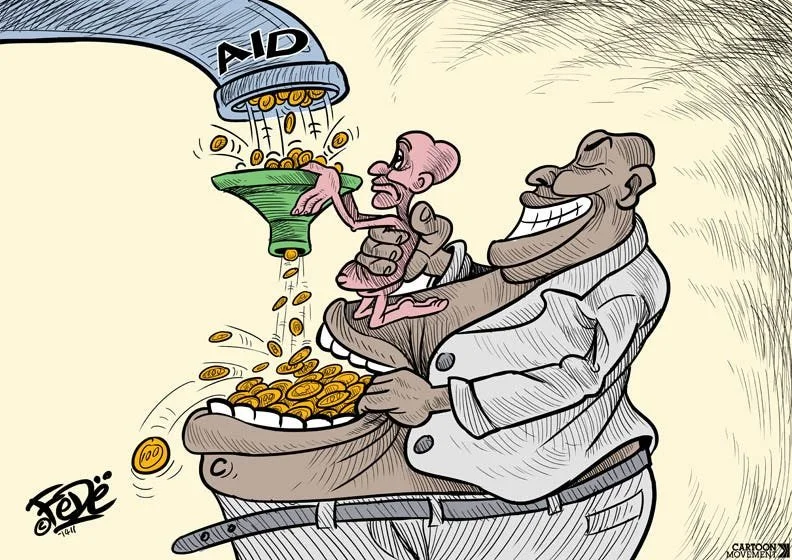
What are the issues that the cartoonist is highlighting?
Case study: Lack of infrastructure is a barrier to development
Weak public institutions, corruption, and political instability are some of the factors that contribute to the infrastructure deficit in LEDC's.
Insufficient infrastructure, such as roads, bridges, and access to transport services, makes it difficult for people to access markets, hindering economic growth.
When infrastructure does not operate effectively, it disrupts the chain of production, leading to economic deficits and decreasing the standard of living.
To do: Investigate the impact of a lack of infrastructure in Chad.
Introduce Chad. Include a map.
List the reasons for Chad’s lack of infrastructure
Annotate maps of Chad’s electrical and roads infrastructure
Describe the status of the following services in Chad.
Electricity and water services
Transport
Communications
How does the lack of infrastructure in Chad influence development?
'Infrastructure is the basic equipment and structures such as roads and bridges that are needed for a country, region to function properly. Infrastructure contributes to development by increasing productivity and providing services. The services generated as a result of an adequate infrastructure base will translate to an increase in aggregate output. For example, improved roads and water and irrigation projects increased agricultural output. While sea ports, rail links and electrical generation, transmission and distribution allow the development of industry and domestic services.
Activity 4. Development is not evenly distributed
Indicators have limitations
Many indices that are used to calculate development are averages for the whole population.
This method means that you cannot see any regional inequalities (disparities) within a country’s population.
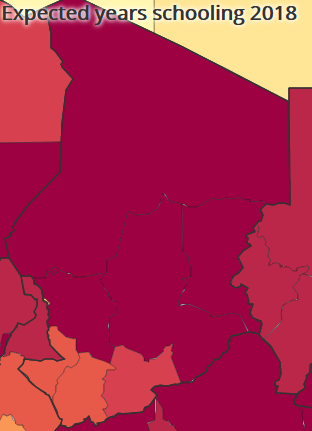
We are going to examine the education indicators for Chad to look at how indicators can be misleading.
To do: Examine disparities in Chad
Use the following indicators to describe the disparities in education indicators in Chad
Search Google for the Mean Years of Schooling for Cambodia.
Describe the trend in Mean Years of Schooling in Cambodia
Use UNESCO to identify disparities in access to education in Cambodia
Use Global data lab to examine access to education in Cambodia using a choropleth map.
3. Consequences of a lack of development
What does a lack of development look like?
A lack of development leads to poor health, low education, limited job opportunities and persistent poverty. Communities may experience food insecurity, unsafe housing, and limited access to clean water and healthcare. Lack of development increases vulnerability to conflict, environmental disasters and social instability, trapping people in a cycle of disadvantage.
Kibera is a slum in the city of Nairobi (Kenya) with approximately 170,000 - 250,000 people
Have a walk around.
Street survey questions:
What are the main building materials?
Do the residents have electricity?
Describe the sanitation in Kibera
What are the risks associated with this?
How do people get water?
Describe the commerce in this area of the slum.
Activity 5. Visualising a lack of development with Dollar street.
What is life like in an LEDC?
To do: Create a case study of the daily life of a family in an LEDC.
Use Dollar Street to examine the lives of a family in an LEDC.
Use photos and quotes to give a sense of the life and aspirations of your family.
Family portrait
Toilet
Bed
Kitchen
Water
House
3. Is inequality inevitable? Discuss
Development varies widely between countries and within communities. These differences in development shape people’s opportunities, wellbeing and quality of life.
We are going to have a class debate that looks at the difficult question.
Is inequality inevitable?
Questions to get you thinking
What factors most strongly influence a country’s level of development, and why?
How do differences in development affect people’s daily lives and opportunities?
Why do some countries progress faster than others?
Which development indicators best reveal inequality?
How might development patterns create disparities within and between countries?