Biomes
A biome is a large area on Earth that has a specific climate, plants, and animals. Think of it as a big neighbourhood where everything living there is adapted to the environment.
Biomes are important because they help us understand the diversity of life on Earth. Each biome supports different kinds of plants and animals, and they all play a role in the planet's ecosystem. By studying biomes, we can learn how living things adapt to their environment and how they interact with each other.
Biome Fun Fact
Did you know that the Amazon Rainforest biome is so dense that it produces 20% of the world's oxygen? It is often called the "lungs of the Earth"!
Geographers define Biomes using abiotic factors:
1. Climate
2. Relief
3. Soils
4. Productivity
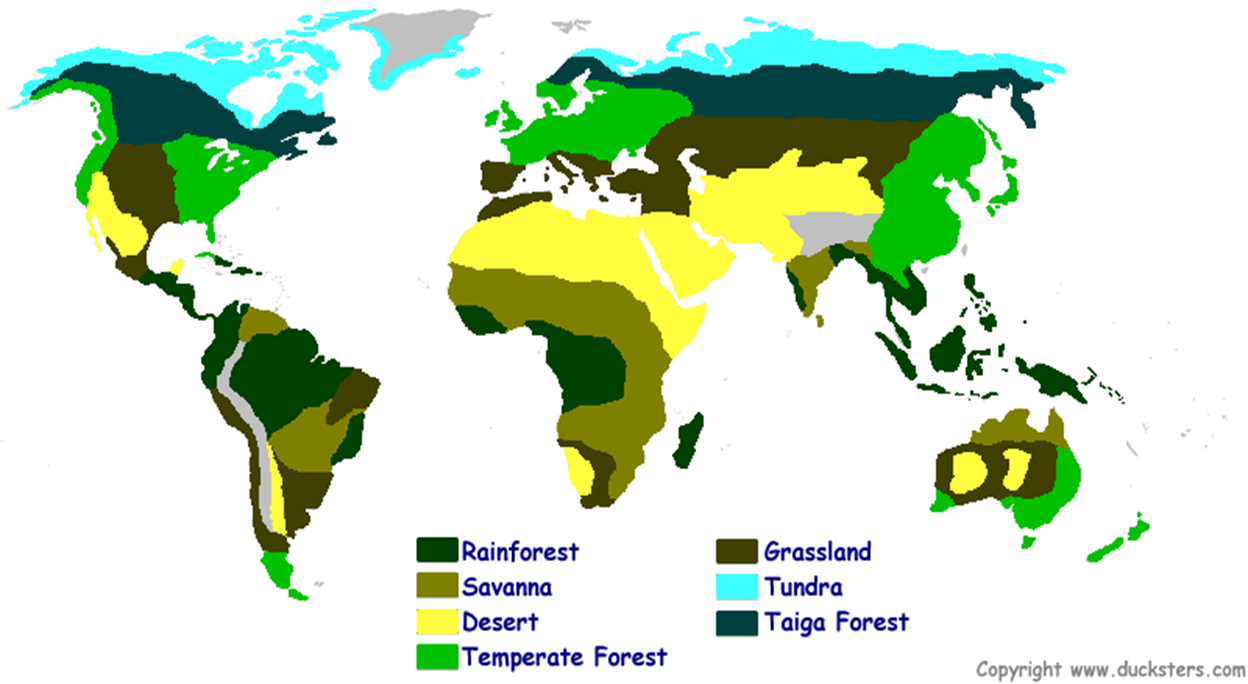
There are five major Biomes
There are several different types of biomes, each with its own unique characteristics
Desert Biome
Aquatic Biome
Tundra Biome
Forest Biome
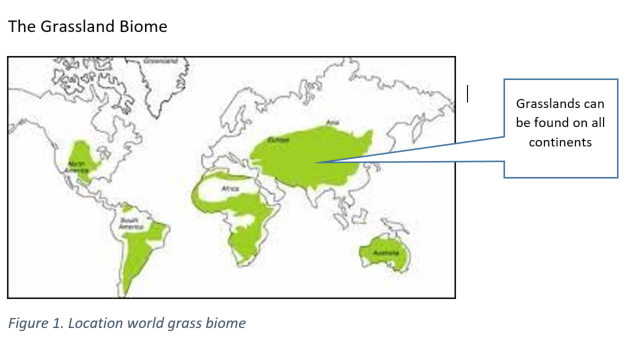
Grassland Biome
To do: questions
Define an abiotic factor.
Define a biotic factor.
List five extra biomes (not the 5 major biomes)
Annotate a map of the worlds biomes. Which biome is Adelaide in?
1. Biome fieldwork
Field work is an important component of the study of Geography.
Unfortunately our proposal for a world tour of the earths Biomes is still under consideration.
The following is a virtual example of what we had planned.
Answer the questions for each station.
Key ideas
Adaptions that plants and animals have made to living in their biomes.
How climate factors determine the nature of the biome
The impact that climate has on the productivity of biomes
Activity 1. Biome virtual fieldwork
Work through the following four stations to examine how biomes are shaped by climate.
Station 1. Animal adaptions
To do: Animal biome adaptions
Watch the slideshow and identify which Biome where each of these animals be found?
Include a description of the climate and environment each animal has adapted to in your answer.
Station 2. Plant adaptions
To do: Plant biome adaptions
Watch the slideshow and identify which Biome where each of these plants can be found?
Include a description of the climate and environment each plant has adapted to in your answer.
Station 3. Climate factors
To do: Climate factors
Watch the slideshow and identify the climate factors that shape the Biome.
Use the climate keywords.
Rainfall
Temperature
Seasonal Variation (Length of growing season)
Humidity
Brain break: David Attenborough - Iguana Vs Snakes
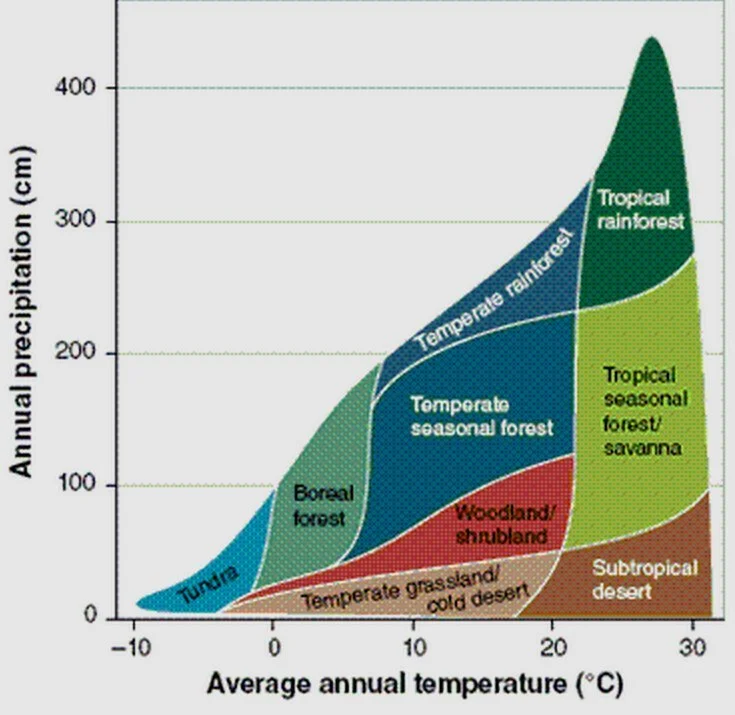
Station 4. Biomass (Productivity) and Climate
To do: Refer to the climate graph to answer the following questions.
Which Biomes have the lowest rainfall?
Which Biomes have the highest rainfall?
What is the main climate difference between the desert and the tundra?
Which Biomes have the highest temperature?
Which Biomes have the lowest temperature?
Which do you think is the most productive Biome? Why?
2. Biome Location Scout
Activity 2. Documentary Location Scout with David Attenborough
The BBC is going to do a documentary on Biomes of the World.
The producers have asked you to scout locations.
Include the following information in your report:
A global map showing the general location of your biome
A description of the defining climatic factors. Include a climate graph to illustrate your description. (When is the best time of the year to film?)
Examples of farming and other human land uses suitable to the biome.
Five (5) location countries that we can use for filming labelled on a map.
Mr. Attenborough has asked that you also write a brief summary of the vegetation and fauna communities the crew can expect to find in your chosen Biome including suggested species.
See Blue Planet Biomes for extra background.
Ensure you label your photos and annotate them
3.The Human Impact - Deforestation
Activity 3. What is deforestation?
Human activities including farming, forestry and mining directly impact Biomes. Forest biomes are impacted by deforestation, the clearing of forests for agriculture, grazing, urbanisation, fuel or construction. Deforestation and forest degradation are the biggest threats to forests worldwide.
Over half of global tropical forests have been destroyed since the 1960s, and every second, more than one hectare of tropical forests is destroyed or drastically degraded. The degradation and loss of forests threatens the survival of many species, and reduces the ability of forest biomes to provide essential services.
Deforestation and forest degradation impact the lives of 1.6 billion people whose livelihoods depend on forests. One billion of them are among the world’s poorest.
To do: Deforestation questions
Define deforestation
List the main causes of deforestation
Include a labelled map of world deforestation.
What are the risks resulting from the degradation and loss of forests?
Deforestation for palm oil production
In Malaysia and Indonesia, forests are cut down to make way for producing palm oil, which can be found in around 50% of products consumers purchase and use on a daily basis, everything from shampoo to banana cake. Palm oil trees flourish in the humid tropics and produce a high yield when grown in equatorial regions.
According to the WWF, palm oil production is leading to loss of critical habitat for endangered species
The biggest impact of unsustainable palm oil production is the large-scale devastation of tropical forests. This leads to widespread habitat loss for endangered species like Asian rhinos, elephants, tigers and orangutans. For example, within Tesso Nilo National Park in Indonesia, that was established to provide habitat for the endangered Sumatran tiger, 43% of the park has been overrun with illegal palm oil plantings.
To do: The Palm Oil industry questions
List and describe the environmental impacts of the growth of the palm oil industry. Include pictures to illustrate your findings
Which countries are the major producers of palm oil? Include a graph to illustrate your answer.
What are the main uses of palm oil?
Which Biome is most affected by the development of the palm oil industry? Include a map of the world’s palm oil growing regions to illustrate your answer.
List the countries where palm oil production is growing fastest.
Explain why you think farmers want to plant oil palm plantations? Provide 2 reasons